Stomatitis is a mouth problem that can cause irritating indications if not treated: how about we discover how to forestall it because of straightforward measures and normal cures. Stomatitis is an aggravation of the mouth, including the gums, the sense of taste, the inward piece of the lips, and the tongue. Stomatitis can have some causes, including helpless sustenance or bacterial contaminations, frequently joined by severe infection and rankles. We should find regular solutions for forestall and treat it.
What Is Stomatitis
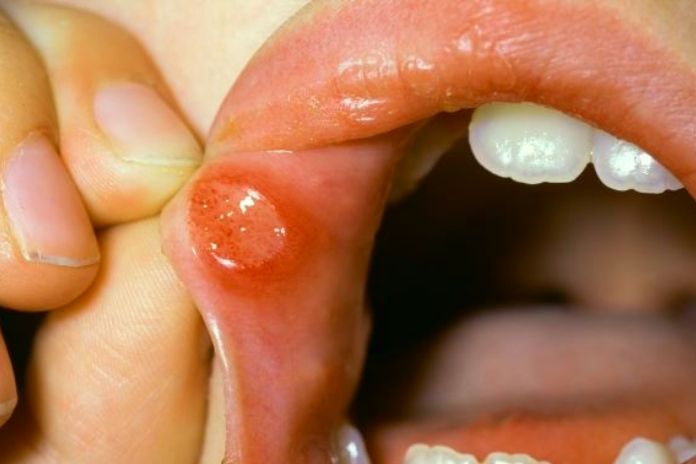
If aphthae is a small ulcer located on the mucous membrane of the mouth, stomatitis is an inflammatory condition of the mucosa itself. Often the two disorders are associated and consequential. Stomatitis can affect men, women, the elderly, and children. People with stomatitis feel pain, accompanied by difficulty in chewing and swallowing, redness and swelling of the gums and tongue, and pain when brushing the teeth. Even blood loss may occur.
Forms Of Stomatitis
There are various forms of stomatitis with peculiar characteristics:
- Aphthous stomatitis: generally affects children and originates from unboiled sheep or bovine milk of animals affected by foot and mouth disease and from exanthematous diseases of digestive disorders. It brings weakness and fever and is manifested by swelling of the cheeks, tongue and the formation of painful blisters.
- Simple catarrhal stomatitis: it presents with redness of some points of the oral mucosa, increased salivation with the formation of small fissures on the sides of the mouth. The tongue appears covered with a grainy yellowish patina, with a dry mouth and burning throat on swallowing.
- Ulcerative stomatitis: this is a lesion of the mucous membrane with necrosis near the gums. It easily extends to the cheeks, lips, tongue, and tonsils. A microbial infection causes it by poor hygiene or intoxication.
- Antibiotic stomatitis: the intake of broad-spectrum antibiotics impoverishes the bacterial flora and impoverishes the amounts of vitamin B. The oral mucosa is impoverished with the fall of the lingual epithelium, and pathogenic germs with inflammatory lesions are colonized.
- Herpetic stomatitis: generally accompanied by a pharyngeal disease and manifested by herpetic lesions on the entire oral mucosa, with a high fever. It typically affects children and is caused by the herpes virus, with the appearance of blisters that sometimes ulcerate with bleeding on the gums, tongue, and palate.
Symptoms
The specific symptoms are related to the forms of stomatitis described, but in general, it manifests itself with
- Pain in the mouth;
- increased salivation;
- formation of ulcerative vesicles;
- redness, canker sores on the tongue and gums;
- halitosis.
The Causes Of Stomatitis
The reasons that lead to stomatitis are unique; most importantly, there are viral and bacterial causes, which start from the oral depression; besides, other potential causes are expected nutrient inadequacies, explicitly nutrients B1, B6, and B12. Dental caries, irresistible illnesses that push down the safe framework, and the admission of anti-infection agents that debilitate the body can likewise prompt the presence of stomatitis.
How Long Does Stomatitis Last
The duration of stomatitis is linked to the form of inflammation manifested. Generally, the symptoms from peak to remission last about ten days, with total recovery within 20 days.
Is Stomatitis Contagious?
The answer is yes, especially in the case of herpetic and aphthous stomatitis, even if the opinions are different. The vehicle of contagion is from salivary contact, and especially in children, it is easy to transmit.
How To Cure
We can intervene on the causes and symptoms of stomatitis with natural remedies that soothe inflammation, rebalance the vitamin intake, and counteract the viral load.
- Vitamin B and Vitamin C are taken through nutrition and vitamin supplements for their immunostimulating and antioxidant capacity; they help the healing process and remission from stomatitis.
- Sage: Sage has antibacterial, antiseptic, and healing properties. An infusion of sage helps to soothe the mucous membranes, clean the tongue, strengthen the gums and counteract bad breath. Rinsing with water and warm sage several times a day helps to rebalance the environment of the oral cavity.
- Sodium bicarbonate: with alkalizing properties, it counteracts inflammation, disinfects the oral cavity, helps decongest the blisters, and relieves pain.
- Lemon: lemon juice also helps to balance inflammation, disinfects mucous membranes, and heals ulcerative lesions.
How To Prevent Stomatitis
Prevention plays a key role. So here are the natural remedies that we can put in place to remedy this annoying disorder.
- First of all, take care of oral hygiene. Poor dental hygiene can cause the appearance of stomatitis and metabolic alterations – which is why good food hygiene is also essential – can cause them. Brush teeth thoroughly and gently, flossing where necessary and having natural mouthwashes on hand.
- Taking care of your diet means controlling what you eat well: avoiding spicy, too acidic, too cold, or too hot foods for a while. Eliminate alcohol anyway, obviously if you also smoke cigarettes. Increase the dose of fruits and vegetables of foods that contain B vitamins, iron, vitamin C, and folic acid. Greenlight, therefore, to anti-inflammatory foods, legumes, and whole grains.
- Thanks to the presence of tannic acid, black tea is considered an excellent natural remedy. Infuse a sachet, let it cool, then place it for a few minutes on the painful points.
- Other rinses can be done with a few drops of tea tree oil, an effective antibacterial, used as a natural mouthwash, or with tepid herbal teas based on sage, thyme, cloves, and nettle.
ALSO READ: 15 HEALTHY FIBER SUPPLIERS THAT WILL KEEP YOU FULL FOR A LONG TIME